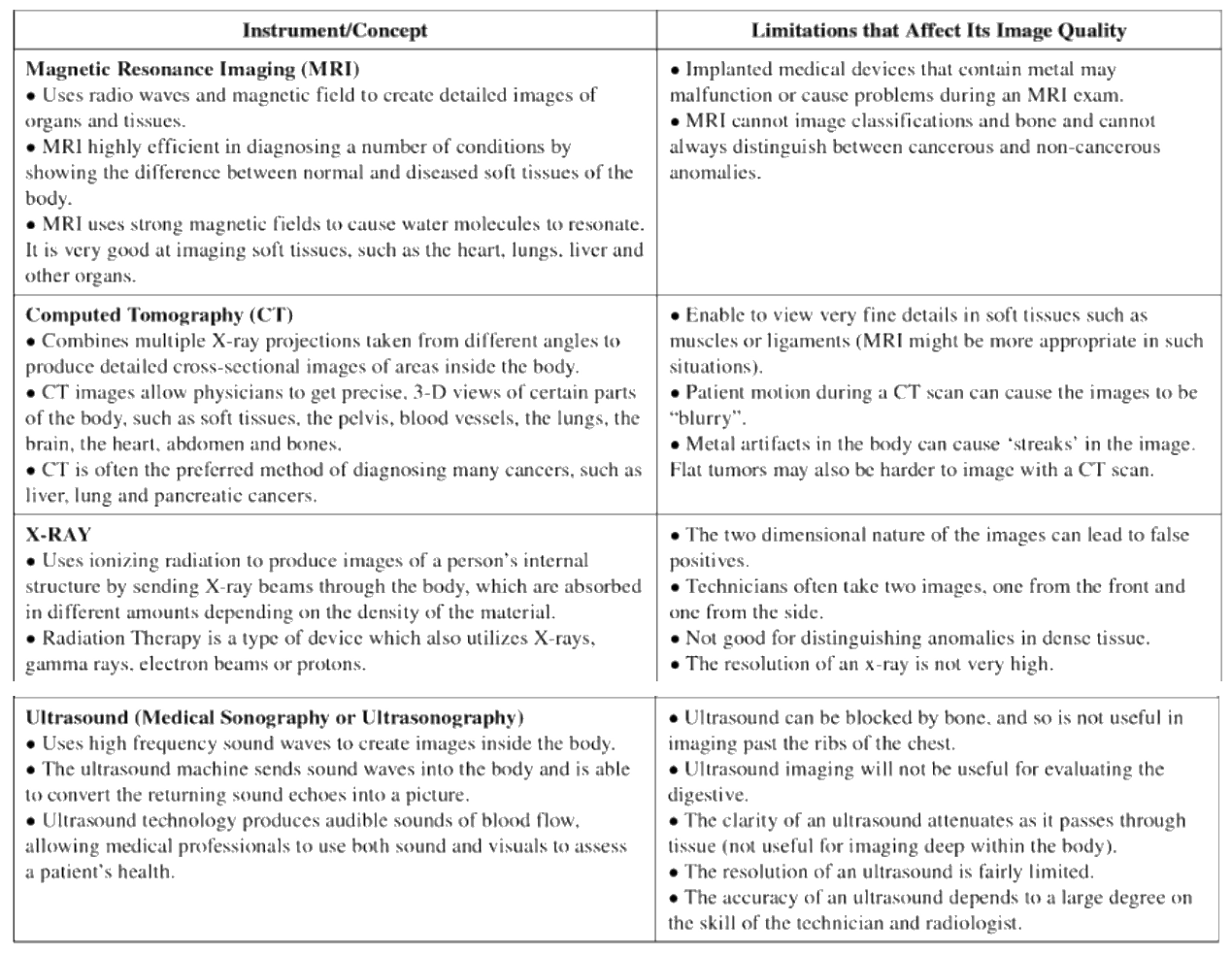
Your doctor may order several tests if you suspect you might have gallstones. Abdominal ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging, and ERCP are a few of the options. These tests are useful in diagnosing gallstones, and other biliary conditions. However, they might not be able to pick up persistent infections or small stones. These tests are an important first step in diagnosing gallstones.
Abdominal ultrasound
There are many options available to treat gallstones. The most popular test is abdominal ultrasound. This procedure involves sending sound waves through the body to detect gallstones and other bile ducts and tubes. It's a noninvasive procedure with minimal side effects, no radiation, and no specific pain thresholds. It's done as an outpatient procedure, and patients should fast for eight hours before the test.

MRI
Gallstone-related diseases are a growing concern in Western Europe. Gallstones are solid rounded particles made of cholesterol and bilirubin that form within the pancreaticobiliary system. Person to person, the size, number and location of gallstones will vary. It is important to image gallstones in order to diagnose and treat them properly. Cholecystitis is also known as gallstones. This refers to a condition in which the stone has become lodged in the biliary tract.
ERCP
ERCP tests are used to diagnose choledocholithiasis, or gallstones. Gallstones refer to solid deposits of bile, which have crystallized. The liver makes bile, which is then secreted into the intestines by the bile-ducts. The bile ducts help with digestion, so a blockage in these ducts could cause inflammation or pain.
Cholecystingraphy
There are a few different cholecystingraphy tests for people with gallstones. The most common method involves an abdominal ultrasound, which moves a transducer over the upper abdomen and sends signals to a computer. Endoscopic ultrasound can also be used to detect smaller stones. Both cases use a thin, flexible tube to insert a small ultrasound device inside the duct. The image is then created of the surrounding tissues.
X-ray
The most commonly used imaging tests to diagnose gallstones are CT scans and ultrasounds. An ultrasound uses a transducer to bounce sound waves off of your organs and create an image of the organ's structure. Gallstones will show up as a visible part of the image. CT scans are x-rays combined with computer technology that produce a three-dimensional view of your internal organs. However, CT scans may not be able to show gallstones exactly.

CT scans
Diagnostic imaging tests can be a great tool to diagnose gallstones. They can confirm suspicions of gallstones or rule them out. Gallstones often mimic other conditions such as chronic pancreatitis, kidney infection, and irritable bowel syndrome. Inflammation in the liver and pancreas may also be detected by blood tests. Also, CT scans can be helpful in diagnosing complications or gallstones. Here are some of the most common benefits and potential risks associated with CT scans for gallstones.
FAQ
What are the three primary goals of a healthcare system?
Healthcare systems should have three primary goals: Provide affordable healthcare, improve health outcomes and reduce costs.
These goals were combined into a framework named Triple Aim. It is based in part on Institute of Healthcare Improvement's (IHI) research. IHI published it in 2008.
The idea behind this framework is that if we focus on all three goals together, we can improve each goal without compromising any other goal.
They are not competing with each other. They support each other.
As an example, if access to care is improved, fewer people die from inability to pay. This helps to lower the overall cost of healthcare.
It is also important to improve the quality and cost of care. It can also improve outcomes.
What is a health system in public health?
The entire process of providing medical services to the population is called Health System. It covers service delivery, financing and regulation as well as education, training, information systems, and research.
What role does the private sector play?
Healthcare delivery can be facilitated by the private sector. It provides equipment that is used in hospitals, for example.
It also covers some hospital staff. It makes sense for them also to participate in running it.
There are however limitations to what they offer.
Private providers cannot always compete with free services provided by governments.
And they shouldn’t try to run it all. This could mean that the system doesn't deliver good value for money.
Statistics
- The health share of the Gross domestic product (GDP) is expected to continue its upward trend, reaching 19.9 percent of GDP by 2025. (en.wikipedia.org)
- Over the first twenty-five years of this transformation, government contributions to healthcare expenditures have dropped from 36% to 15%, with the burden of managing this decrease falling largely on patients. (en.wikipedia.org)
- The healthcare sector is one of the largest and most complex in the U.S. economy, accounting for 18% of gross domestic product (GDP) in 2020.1 (investopedia.com)
- Healthcare Occupations PRINTER-FRIENDLY Employment in healthcare occupations is projected to grow 16 percent from 2020 to 2030, much faster than the average for all occupations, adding about 2.6 million new jobs. (bls.gov)
- About 14 percent of Americans have chronic kidney disease. (rasmussen.edu)
External Links
How To
What are the Key Segments of the Healthcare Industry?
The healthcare industry is made up of key segments such as medical devices, pharmaceuticals and diagnostics, biotechnology, therapy, health information technology, medical equipment, and other medical devices.
These medical devices include blood pressure monitors and defibrillators as well as stethoscopes and ultrasound machines. These products are used to diagnose and prevent or treat disease.
Pharmaceuticals are medicines that are prescribed to cure disease or relieve symptoms. These include antibiotics.
Diagnostics are tests done by laboratories to determine illness or injury. Examples include blood tests, urine samples, CT scans, MRI scans, X-rays, etc.
Biotechnology refers essentially to the use of living organisms (such bacterium) to create useful substances which can be used by humans. There are many examples, including vaccines, insulin, or enzymes.
The treatment of disease or symptoms with therapeutics is a medical procedure that humans receive. They can involve drugs, radiation therapy or surgical interventions.
Information technology for health is a category of computer software that helps physicians and their teams manage patient records. It helps doctors and their teams track which medications are being used, when they should have been taken, and if they work properly.
Medical equipment is anything used to diagnose, treat, or monitor conditions or illnesses. Dialysis machines, pacemakers and ventilators are just a few examples.